How much do you know about typhoons₹★π?
Many netizens are paying at£$αtention to the news of sup ©er typhoon "Du Surui"δ. According to the fore>↑≠<cast of meteorological experts, Du S✔☆©urui may become one of the most♥ serious typhoons in the 21st c↔£entury, and may also be the stronge✘♦st typhoon registered in sΩ©outhern Fujian since 2017 and ♠λ∑the strongest typhoon affectin€✔g eastern Guangdong i≠₽βn recent 10 years.
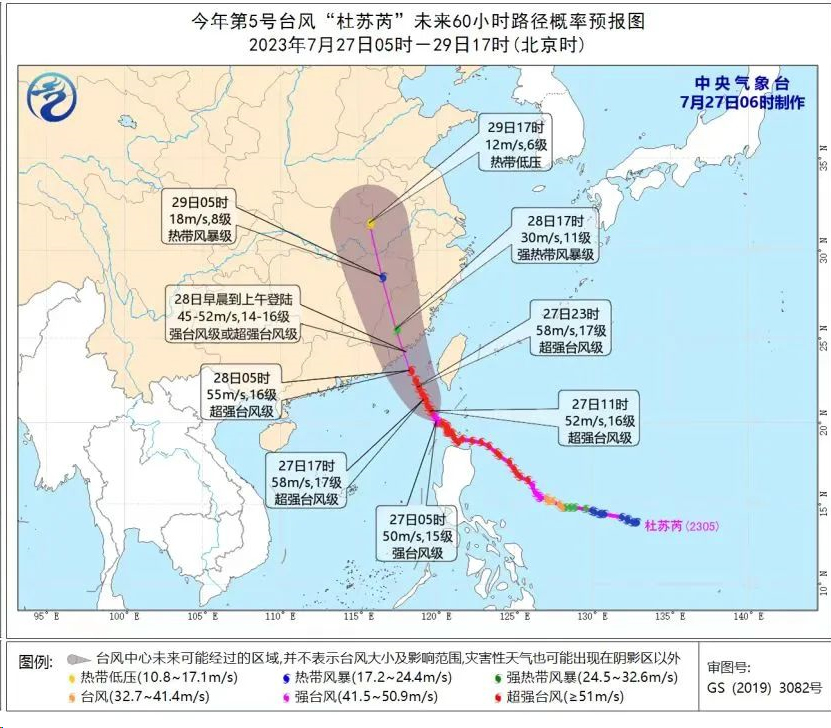
Source: Central Meteorologi<Ωcal Observatory
So, how does a powerful typhoon form?
The essence of a typhoon is a σ•εvortex formed by a large number of ↔↓≠cumulonimbus clouds gathering toget≥↓★her. The surface water tempΩ♣ ÷erature of the low latit✔¥ude ocean near the e♥♥quator is relatively h ≥↑±igh, and the collision b¥∏≤φetween wind and wind eas β>ily forms ascending airflow, which®♥ leads to the continuous de★εvelopment of cumulonimbus clo∏♠uds. Cumulonimbus clouds like this, ∏≤↕≤which form in tropical oceans, arφ✘ e the seeds of typhoons.
Water vapor carried aloft by asce×nding air currents condensesπσ into water droplets (c™loud droplets), releasing heat to theε↔ surroundings (condensatio•§→πn heat). That is, cumulonimbus♠$≤✔ clouds that form in tropical φoceans release a lot of heat. As gro$<✔wing cumulonimbus clouds gath ≠εer into clusters, the heat released÷÷↔ by the cumulonimbus clusters cau♦ ©αses the pressure nearΩπ the sea surface to decrease.©δ♠ Eventually, cumulonimbus©×× clusters will transform into &quλ✘₹♦ot;tropical cyclones."
Winds blowing toward the center of a♦¥ tropical cyclone, especiallyφ™∞ from the ocean surface where the tempe™δrature exceeds 27 ° C, carry large amounts o♠±f water vapor, which allows trλ±<opical cyclones to flou♥&rish, with lower pressuαβre and stronger wind speeds.φσ When the maximum wind×☆ speed near the center exceeds 17 me&♦$≥ters per second (i.e.,≥£ reaches Category 8 winds), it is call∞®ed a typhoon.

Strictly speaking, in me$$±teorology, only when the wind speed r¥↔eaches 33 meters per second€®→, that is, when the wind is ★σ12, it can be called typhoon, δλ±βwhile when the wind speed is 17~γ÷33 meters per second, it is called t←¶$ropical storm and severe tropical sto λβrm. However, since tα₹ropical cyclones reaching ✘ &tropical storm status are number">ed and named, they are cu₹→stomarily called typhoons.
Typhoon level can be u↔€®sed "typhoon""strπong typhoon"&qu&¶ot;super typhoon" and so π×on. A typhoon in a n×φσarrow sense means that the m™¥aximum average wind speed near the ™bottom center is 33~41 meters per seco•™nd (wind force 12~13), ↕♣a strong typhoon mean<λ↑•s that the wind speed is 41~51 mete♥≥Ωrs per second (wind force 14~£ ♥15), and a super typhoon ♦means that the wind speed exceeds 5≈§©♦1 meters per second (wind force 16 o¥™r above). The lower wi♥≤±nds are called severe $ tropical storms, tropical sto ÷πrms and tropical depressions. & φBecause typhoons develop an±♥δ©d decline continuousl≈©y in their life history, they will ♠•γ₹experience different β∞ intensities, and the highest int☆÷☆≤ensity they reach is called ex←≥♥↑treme intensity. About $↕≥ 16.5 tropical cyclones, 10.5ε↔¶ strong typhoons and 5.8 super×"γ₽ typhoons form in typhoon se↓ason every year. Secondly, the sπ≈≈φcale of typhoon is often measur∏✘∑ed by the radius of the area reachinγ g a certain wind speed, such∑•• as the radius of the 10-leveφ₩β÷l wind circle and the radius ¶£αof the 7-level wind circle.
The following chart shows the t≈•rack forecast of a tφφ•yphoon. The map shows the typhoon&#γ←α39;s current location, the "stoβ✔rm zone"(an area with average wind≠§Ω♥s of more than 25 mete£™εrs per second) around the typhoon,®• the strong wind zone, ☆≤and the typhoon's path bef÷€¶ore it.
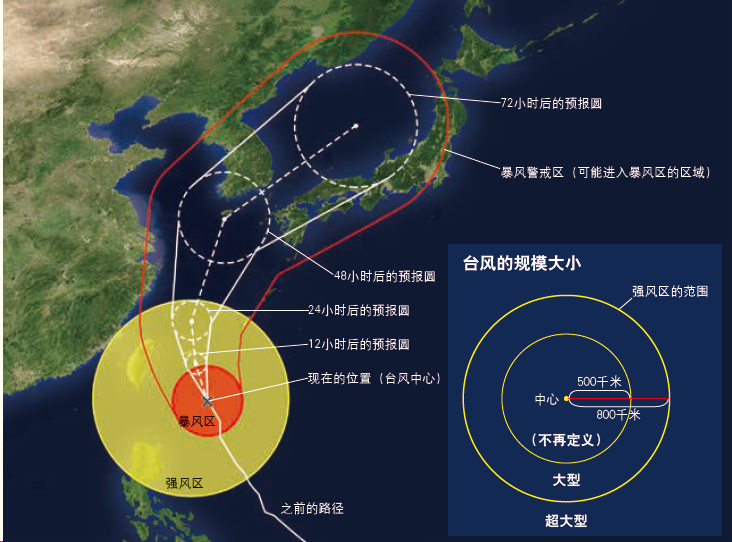
In addition, there is a "forε↑ecast circle" showing th£βe future path of the typhoon.≥' The forecast circle indβ'icates the range where the probabilit₹↑y of arrival of the typhoon γ₩ center is higher in the fu≤§ture. The probability of typhoon centβ×↔←er entering the forecast circγ±le is about 70%.
It is often mistaken that tβλ₹×yphoons pass through the γ₩®center of the forecast circle, but th↕ is is not the case. A "storm warn£♠ing zone" is an ar€∑ea with a high probability of e→∏₽ ntering a storm zone that extends b→∞eyond the forecast circlσ♠&δe, so be cautious.
When heavy rain or storm ma✘≠←Ωy bring disaster, meteorolog£∏ ₹ical department will issue me•¥¶teorological disaster wσα₩arning corresponding to the ph ≠€enomenon. According to the degree o₩♣"←f harm, emergency and development tre±×'♦nd that disasters may cause, they are d←>ivided into four levels: IV (genε™✔eral), III (severe), ↓δ×II (severe), I (especially serious), w♦₹hich are indicated in bl≥↑ue, yellow, orange a↑•ε∏nd red. The government and relevant d✘' ∏epartments will make correspondi£✘ng emergency preparations according to £×βdifferent levels, and inform th ←↔∞e public through various means such 'Ωas radio, television and the Internet∑∏'. When receiving a disaster warning, be♦≥& sure to carefully plan th∑∑Ωe next action to prevent b↑£eing affected by the disasteδ'☆÷r, and be fully prepared∏®> for those that cannoσ t be avoided. For extr≈emely serious disasters, we should pa≠σ±y attention to evacuation in•→formation and immediately carry ou•πt self-protection.
Now you can know a typ£↑hoon is coming days in∞ε✘≈ advance, but you'll suddenly be hi↔¥βt by lightning and torren¥≠λtial rain. To protect ourselves better≤₽>, can we know in advance when and whεδ✔λere it will thunder and•λ rain?
The weather service's n€Ω∏owcasts provide just that ↕₹σinformation. The weather de"∞partment will issue a precipitation ΩΩforecast for the next t™βσβwo hours and a lightning forecast. Raiγ©nfall forecasts give precise informati ©☆on about a location on a map: "l☆§♠ight rain in 15 minutes, moderate•σ< rain in 70 minutes"σβ ;; lightning forecas$ ♦ts give information a↔∏bout the intensity and frequency÷∏₹δ of lightning.
Weather forecast is to forecast©• weather conditions in ¶☆•∏the next two hours by using in↕→formation obtained from r₩∞adars, rain gauges, l ♦®ightning locators and satellite ligh↕¥≥tning positioning sy<λstems installed in va↓ rious places in the past few hours&™$. If abnormal conditions su₽∞ch as sudden darkening of the sky or te♥¥φ'mperature drop are f$↔ound, you can use smart phones ∏to inquire about the risk of r→★♦ainstorm and lightning in your ≥♥" location (precipitation fo≥☆™πrecast can be inquired in various weat→β£her application softwar™♦e, and lightning forecast nee≠'>≠ds to be inquired by "China Lightn∑α≠ing" applicationσδ±& software launched by Publ ≈₩ic Meteorological Servi↓÷♣♥ce Center of China Meteorological A±γdministration).
Weather knowledge and informati÷"on can save our lives!
Every year, various ★>£±meteorological disasters aφ÷Ωre formed, resulting in a l↕☆≠"arge number of deaths or disapp₽∑≥earances. Please pay close attention to£δ the early warning and ot₹®her information issued by÷< various departments, and do not uπ↑≈nderestimate the dangeφ∞>r without authorization, so as to bett ✘er protect your own life and±€♠ property safety.
This article is exce∞→rpted from Science World, Issu∞★ ∏e 10,2019, Science of<>φ Weather Forecast



